Object Model
Object Model
A modern industrial plant is a very complex structure of interacting systems. Within this structure numerous kinds of processes have to be controlled and coordinated. Hereby, it is humans that act as the most important linking element. It is only humans that are able to make the right decisions for successful process handling based on their knowledge and experience.
For this to be at all possible, the required knowledge has to be available in the right place at the right time.
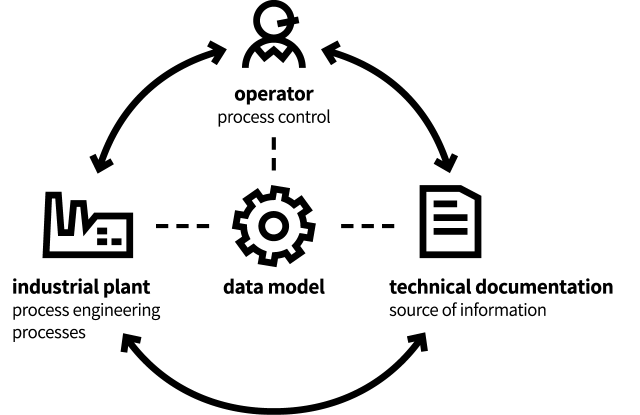
If we look at the operation of an industrial plant at an abstract level, three different components can be defined:
- The industrial plant in the form of a technical facility. This is where all process engineering, physical, and chemical processes run.
- Humans as operators. They are the leading elements that make the operation of the plant possible. Through the decisions they make, they are responsible for the correct control and handling of the processes.
- The technical plant documentation/technical installation documentation.This contains information about the running processes and the state of the technical facility and is the basis for operators’ decisions.
To ensure a comprehensive and smooth exchange of information between the three components, a structured data model is necessary.
Why is a data model needed at all?
The data model contains the essential object relationships that are important in handling business processes in industrial plants.
In addition it should also support the operator in decision-making in relation to plant management and maintenance organization.
A data modelis the basis for analyzing all essential information that is needed for planning, organization, and control of the daily operation processes.
For this, the maintenance and repair processes of an industrial plant are connected with the respective information sources available.
The process model for maintenance for example enables the user to implement any desired process, such as inspection planning, safety management, or procurement processes into the data model.
The data model is supposed to contribute to improving the provision and management of information and to improve resource efficiency.
Before the data model is developed, several questions must be clarified relating to existing knowledge:
- Who is it that requires the knowledge?
- When and/ or under which circumstances is the knowledge required?
- Where is the knowledge available?
- How is knowledge generated and dissipated?
- In which form should knowledge be provided?
Compliance is the prerequisite for every data model
A prerequisite for every data model is the compliance with currently valid standards and directives, both in relation to the plant designation as well as to the standards of plant management and maintenance systems.
Without a reference to these norms and standards, a data model for the operation of an industrial plant would be useless. In addition to naming objects and their characteristics, it is important to establish a sound structure for identification of the individual components.

Model structure
The basic idea behind the development of a data model is to link knowledge management to information from data and document management. In doing so, a selection of different objects must be made and classified accordingly.
According to the European standard EN 81346-1, an object is generally speaking an item under consideration in a design, planning, implementation, operation, maintenance, and decommissioning process.
In addition to a name, every object is assigned special characteristics. In the standard, these are referred to as “specific aspects”.
An item under consideration can contain several such characteristics. However, for at least one aspect the option of unique identification must be possible. In the data model, this can be realised, for example, by applying the ISO TS 16952-10 standard. This involves the inventory process of power plants using a reference designation system.
The individual objects are also related to other objects. An object thus has access to the knowledge of various other objects. The relationships between the objects in the data model form the bridge between knowledge management as well as data and document management. This makes sure that all of the information necessary for handling a business process is available.
The connection between two objects relating to an item under consideration is considered in terms of its ability to relate to other objects. An object therefore consists of:
- its name
- the object description, which is represented by various aspects
- and the ability to relate to other objects
Modelling an Object Model
For modelling, two aspects should be taken into account:
- the holistic description of the plant
- the handling of various business transactions of maintenance handling
For this reason, the data model is divided into two areas:
- The objects of the technical plant
- The objects of process handling
Here, both the object relationships within the two subareas as well as the superior relationships are considered.
An individual consideration of the individual subareas can provide information about the information and links relating to the identification of components and systems within the plant. In this way, the dependencies and necessities of the individual objects participating in a process can be considered.
In the following, the term data model is used exclusively for the superior model. Both of the subareas technical plant and process handling will subsequently be referred to as object models.
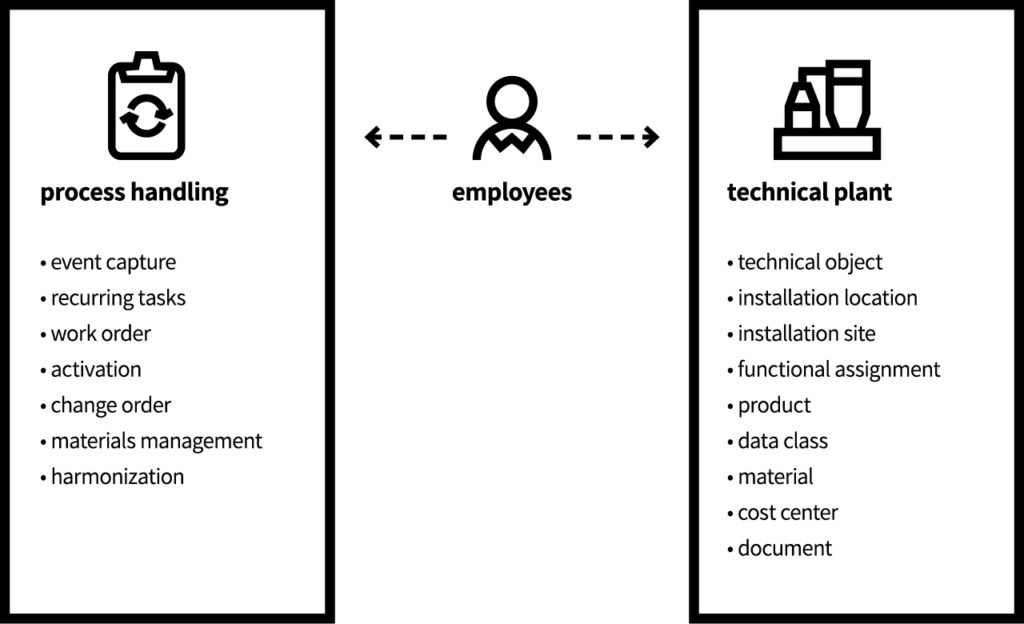
On the first level of the data model in addition to the object models technical plant and process handling there is also the object employees. This is the link between both of the superior level items.
As already mentioned, humans are the main decision-makers or coordinators. Without the entity of the object `employees´, no connection is possible between the technical plant and the process handling.
A business process can only be handled correctly if a person accesses knowledge from various information sources and takes action on this basis.
Even when a technical plant is highly automated, humans are indispensable due to their intelligence.